REGENERATIVE MEDICINE / CELLULAR THERAPY
STEM CELLS / MSCs
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are cells that have the ability to divide indefinitely to differentiate into specific cells and replace those that are lost due to natural wear, injury or disease. Therapy with Mesenchymal Stem Cells is a treatment non-invasive whose objective is to replace damaged cells in the body. This treatment can be applied intravenously or injected locally in specific locations, depending on the patient’s needs.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE / CELLULAR THERAPY
STEM CELLS / MSCs
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are cells that have the ability to divide indefinitely to differentiate into specific cells and replace those that are lost due to natural wear, injury or disease. Therapy with Mesenchymal Stem Cells is a treatment non-invasive whose objective is to replace damaged cells in the body. This treatment can be applied intravenously or injected locally in specific locations, depending on the patient’s needs.

Among the group of stem cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) are undifferentiated cells from adult tissue that have the capacity to self-renew (form cells identical to the cells of origin), as well as to differentiate into different cell lineages, where their Its function is to repair damaged tissue, both under normal conditions and due to aging or disease.
Cell therapy with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) is one of the main resources that the scientific community recognizes to act effectively. It is worth mentioning that many treatments for various diseases are still in the research process. Due to the multipotent capacity and cellular plasticity of these cells, it is intended to recover the function of damaged organs and tissues of the human organism.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of multipotent stromal cell that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (bone cells), chondrocytes (cartilage cells), and adipocytes (fat cells), etc. They are found in multiple tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood, placenta and more.
Characteristics and Functions
Multipotency: MSCs can differentiate into several different types of cells, which makes them valuable for regenerative medicine.
Immunomodulatory Properties: MSCs have the ability to modulate immune responses, which can be beneficial in treating inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration: MSCs play a crucial role in repairing and regenerating damaged tissues due to their ability to differentiate and secrete bioactive molecules that promote healing.
Therapeutic Applications
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) offer a range of benefits due to their unique properties and capabilities. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Tissue Regeneration and Repair
MSCs can differentiate into various cell types, including bone, cartilage, and fat cells. This makes them valuable for repairing and regenerating damaged tissues, particularly in orthopedics (bone and cartilage repair) and wound healing.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
MSCs secrete bioactive molecules that have anti-inflammatory effects. This helps in reducing inflammation and promoting healing in conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other chronic inflammatory conditions.
3. Immunomodulation
MSCs have the ability to modulate the immune system, reducing immune responses that can lead to tissue damage. This property is particularly beneficial in treating autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Promotion of Angiogenesis
MSCs promote the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) by secreting factors that enhance blood flow to damaged tissues. This is particularly useful in treating ischemic conditions such as heart disease and peripheral artery disease.
5. Reduction of Fibrosis
MSCs can reduce fibrosis (the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue) in organs such as the liver and lungs, helping to maintain tissue function and prevent organ failure in conditions like liver cirrhosis and pulmonary fibrosis.
6. Neurological Benefits
MSCs have neuroprotective properties and can support the repair of nervous tissue. They are being investigated for their potential to treat neurodegenerative diseases like Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and spinal cord injuries.
What type of Cell therapy we use in BMC Clinic?
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are distinct types of stem cells with unique properties and potential applications in regenerative medicine. Here are the key differences among them:
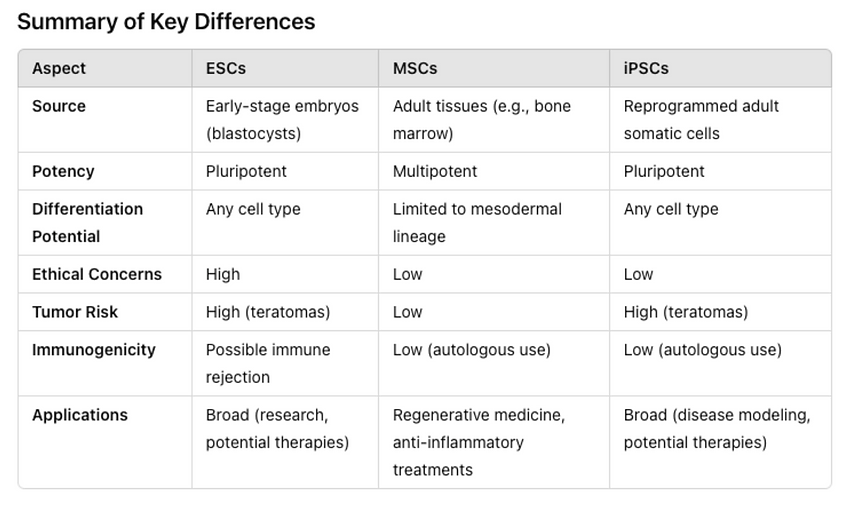
At BMC Clinic we use just Mesenchymal Stem Cells MSCs due to low tumor risk and lo Immunogenicity, Source in various tissues including bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood, and dental pulp.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Potency: Multipotent: Can differentiate into a limited range of cell types, primarily those of mesodermal origin (e.g., osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes).
Characteristics: Strong immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. Lower ethical concerns as they can be harvested from adult tissues. Limited differentiation potential compared to ESCs and iPSCs.
Applications: The use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in antiaging medicine is an emerging field that holds considerable promise due to the unique properties of MSCs, such as their regenerative, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory capabilities. Here are several ways MSCs are being explored in the context of antiaging medicine and precision medicine:
1. Skin Rejuvenation and Aesthetics
Mechanism: MSCs can differentiate into various cell types, including fibroblasts, which are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the skin. They secrete growth factors and cytokines that promote collagen production, enhance skin elasticity, and reduce wrinkles.
Applications: MSCs are used in skin creams, serums, and injectable treatments to promote skin regeneration, reduce signs of aging, and improve overall skin health.
2. Hair Regrowth
Mechanism: MSCs promote the proliferation and differentiation of hair follicle cells. They enhance the local microenvironment of hair follicles, promoting hair growth and preventing hair loss.
Applications: MSC-based therapies are being developed to treat androgenetic alopecia (common baldness) and other hair loss conditions. Capillary microsurgery, restoration and hair transplant with MSCs, exosomes and platelet rich plasma.
3. Joint and Bone Health
Mechanism: MSCs can differentiate into chondrocytes (cartilage cells) and osteoblasts (bone cells), promoting the repair and regeneration of joint and bone tissues. They have anti-inflammatory properties that help alleviate joint pain and reduce inflammation associated with conditions like osteoarthritis.
Applications: MSCs are used in treatments aimed at regenerating cartilage, improving joint function, and reducing pain in patients with degenerative joint diseases.
4. Muscle Regeneration
Mechanism: MSCs secrete growth factors that promote the repair and regeneration of muscle tissues. They help in the recovery of muscle mass and function, which tends to decline with age.
Applications: MSC-based therapies are being investigated for treating sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) and improving muscle function in older adults.
5. Immune System Modulation
Mechanism: MSCs modulate the immune system, reducing chronic inflammation that is often associated with aging and age-related diseases. They help in maintaining a balanced immune response, which is crucial for healthy aging.
Applications: MSCs are being studied for their potential to treat age-related inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, thereby improving overall health and longevity.
6. Neuroprotection and Cognitive Function
Mechanism: MSCs have neuroprotective properties and can promote the repair of neural tissues. They secrete factors that support the survival and function of neurons, potentially improving cognitive function.
Applications: MSC-based therapies are being explored for their potential to treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, as well as to improve cognitive function in aging individuals.
7. Cardiovascular Health
Mechanism: MSCs promote angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) and repair damaged cardiac tissues. They help in maintaining cardiovascular health, which tends to decline with age.
Applications: MSCs are being investigated for their potential to treat heart diseases and improve overall cardiovascular function in older adults.
Conclusion
The use at BMC Clinic, Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in antiaging medicine leverages their regenerative and reparative capabilities to address various aspects of aging, from skin rejuvenation to muscle regeneration and cognitive function. While the potential benefits are significant, it is important to note that many MSC-based therapies are still in the experimental stage. However in BMC Clinic we follow rigorous clinical trials which are necessary to fully understand their efficacy, safety, and long-term effects.
As research progresses, MSCs could become a cornerstone of antiaging therapies, offering new ways to enhance health and longevity.
